
One difference between a somatic reflex, such as the withdrawal reflex, and a visceral reflex, which is an autonomic reflex, is in the efferent branch. Whereas the basic circuit is a reflex arc, there are differences in the structure of those reflexes for the somatic and autonomic systems. The autonomic system, however, targets cardiac and smooth muscle, as well as glandular tissue. Somatic responses are solely based on skeletal muscle contraction. The main difference between the somatic and autonomic systems is in what target tissues are effectors. The autonomic nervous system regulates organ systems through circuits that resemble the reflexes described in the somatic nervous system.
Describe the effects of drugs that affect autonomic function. Determine the effect of the autonomic nervous system on the regulation of the various organ systems on the basis of the signaling molecules involved. Differentiate between short and long reflexes. Explain the differences in sympathetic and parasympathetic reflexes. Compare the structure of somatic and autonomic reflex arcs. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.By the end of this section, you will be able to: The ANS is classically divided into two subsystems: the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) and sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Whereas most of its actions are involuntary, some, such as breathing, work in tandem with the conscious mind. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, salivation, perspiration, pupillary dilation, micturition (urination), and sexual arousal. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system, functioning largely below the level of consciousness and controlling visceral functions. Association nerves integrate sensory input and motor output these nerves number in the thousands. They include information related to smell, vision, eyes, eye muscles, the mouth, taste, ears, the neck, shoulders, and the tongue. Cranial nerves are the nerve fibers that carry information into and out of the brain stem. Spinal nerves are peripheral nerves that carry motor commands and sensory information into the spinal cord. The human nervous system: The major organs and nerves of the human nervous system. The somatic nervous system consists of three parts: The somatic nervous system controls all voluntary muscular systems within the body, and also mediates involuntary reflex arcs. The SoNS consists of efferent nerves responsible for stimulating muscle contraction, including all the non-sensory neurons connected with skeletal muscles and skin. 
The somatic nervous system (SoNS) is the part of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of body movements via skeletal muscles. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
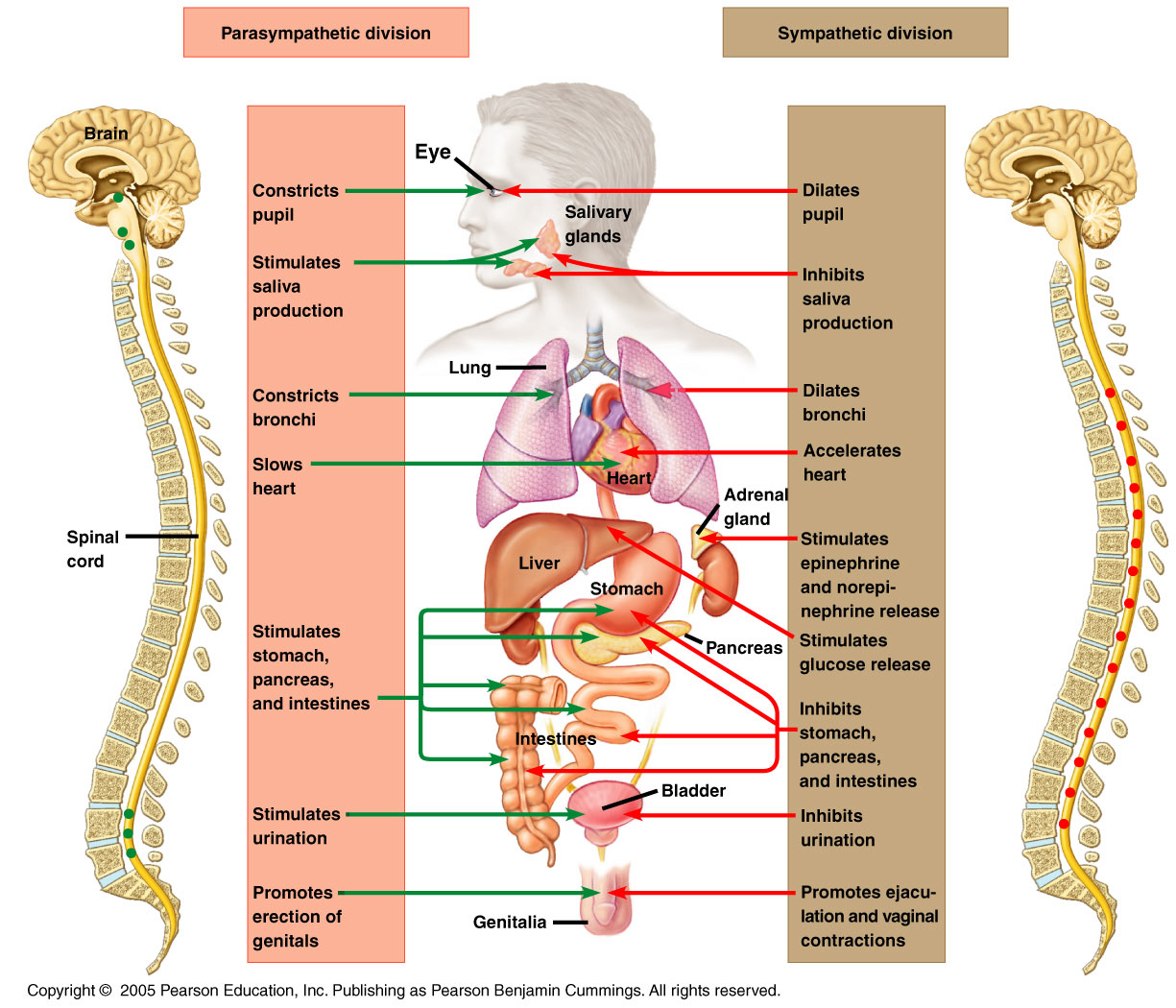
The peripheral nervous system includes both a voluntary, somatic branch and an involuntary branch that regulates visceral functions.Įxamples of body processes controlled by the ANS include heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, salivation, perspiration, pupillary dilation, urination, and sexual arousal.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
